When you need to build something big and heavy like bridges, tall towers, or piers. You must have a strong and stable foundation. Caisson footing is very important in making sure these structures don’t fall or sink into the ground. Imagine trying to build a tall building on soft dirt. It might tilt or fall over because the ground can’t handle its weight. But with caisson footing, builders can create a base deep underground, reaching strong soil or rock that can hold up the entire structure. This foundation can handle a lot of weight and pressure, so the building stays safe and secure.

In this explanation, we will learn more about how caisson footing works and why it’s so important in civil engineering, which is the science of building things like bridges, roads, and towers. Engineers use caisson footings to keep big structures standing tall for a long time, even if the soil isn’t strong on the surface. So, let’s explore how this amazing technique helps us build the world around us!
What is Caisson Footing?
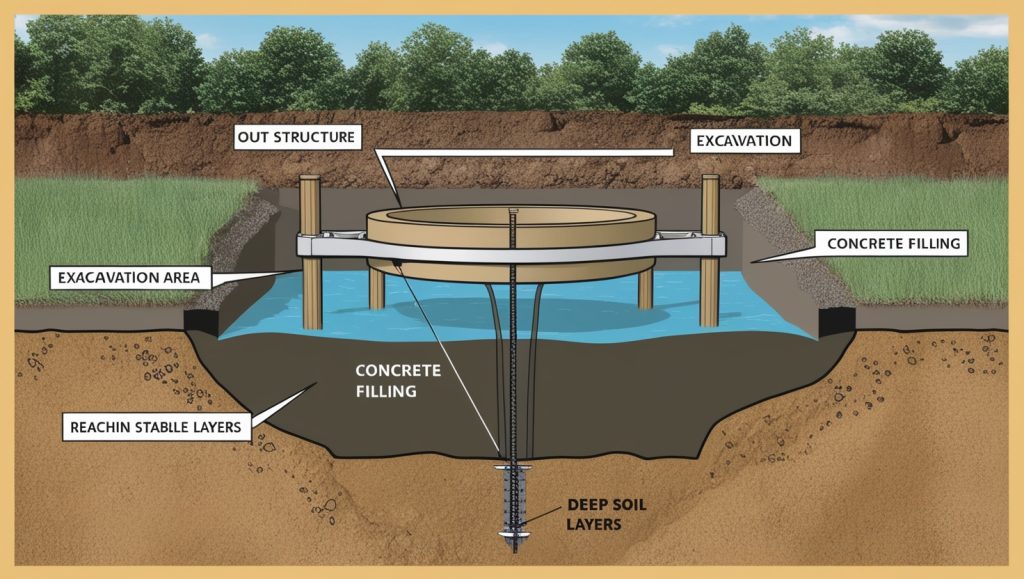
A caisson footing is like a special foundation that builders use when the ground at the surface is not strong enough to hold up a big building or structure. For example, if you try to build something heavy, like a tall tower, on soft soil, it could sink or tilt. To solve this, engineers use caisson footing. Imagine a large, watertight box, kind of like a strong, sealed container. Builders push the caisson deep into the ground until it reaches strong soil or rock that can hold the weight of the building. Once the caisson gets to the strong layer of earth, builders fill it with materials like concrete, which hardens and provides a solid base. This way, the heavy building or structure can safely rest on the foundation, even if the surface soil isn’t very strong.

Caisson footings are super helpful when the ground is weak, especially in places where people need to build in or near water, like rivers or oceans. Imagine you’re building a bridge across a river. The bottom of the river might have soft mud or sand that can’t hold the weight of the bridge. In this case, builders use caisson footings to go deeper into the earth, past the soft mud, to reach a solid layer of rock or hard soil. The caisson footing can hold up very heavy structures, so the bridge doesn’t sink or lean to one side. Over time, caisson footings make sure that the bridge or any other big structure stays straight and strong. This is why engineers use this technique when the ground isn’t strong on the surface.
Types of Caisson Footings
There are many types of caisson footings that builders use, and each one has a special purpose. Some are better for working in water, while others are better for building on soft soil. Builders choose the right kind of caisson depending on what they are building and where they are building it. Now, let’s learn about the most common types of caissons and how they help create strong foundations for structures.
Open Caissons:
An open caisson is a large, hollow tube or cylinder that builders use for big projects like bridges. The bottom of these caissons is open, so workers lower them into the ground and dig out the soil from inside. As the workers remove more soil, the caisson sinks further into the ground. Open caissons help builders work in water, like in rivers or oceans, because they can sink into the ground while giving the bridge or structure a strong foundation.
Box Caissons:
A box caisson is different from an open caisson because it has a closed bottom. Workers make these caissons ahead of time (called prefabricated) and then lower them into the ground. After the box caisson is in place, workers fill it with concrete to make it strong. Builders often use box caissons in places where the soil is soft or muddy, like near the ocean or rivers, to create a strong foundation for things like piers or other marine structures. The closed bottom helps the caisson stay steady in soft ground.
Pneumatic Caissons:
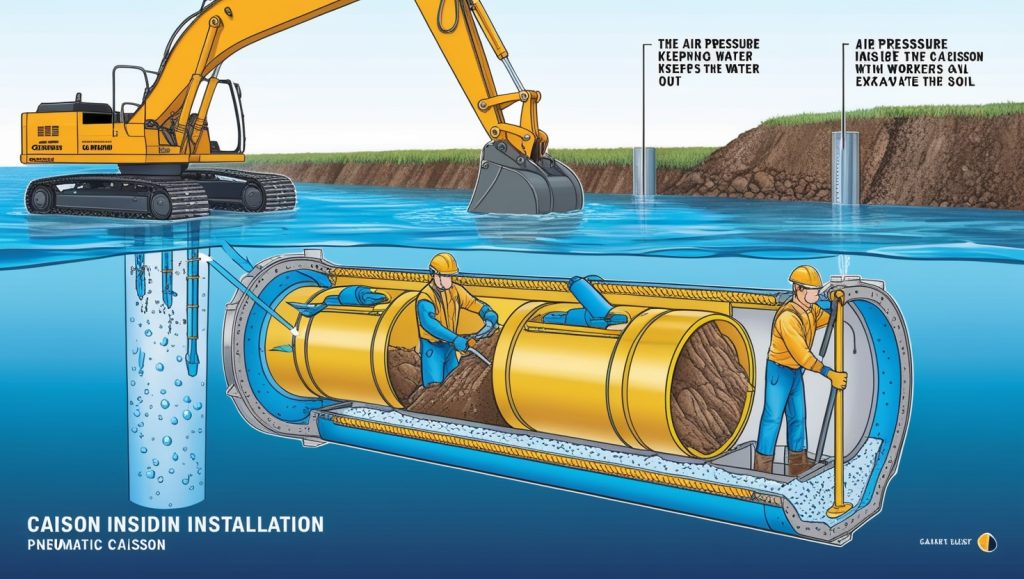
Builders use pneumatic caissons when working underwater. These caissons are special because they have a sealed chamber filled with air, which stops the water from getting inside. Workers can enter this airtight chamber to dig and remove soil, even when they are deep under the water. The caisson stays strong because the air pressure inside it keeps the water out. This type of caisson is important for building underwater, like for bridge piers in rivers or oceans, where workers need to stay dry even though they are surrounded by water.
Floating Caissons:
Builders use floating caissons, also called pontoon caissons, when the ground is too soft or unstable for other footings. These caissons float on water and are moved into place. Once in the right spot, they sink into the ground. After they settle, builders fill the caisson with material to make it a strong foundation. Floating caissons are very useful for building in places where the soil is too weak for regular foundations.
How Caisson Footings Work
The main job of caisson footings is to transfer the weight of a building or structure deep into the ground, where the soil or rock is strong enough to support it. This means the foundation goes far below the surface, where the earth can handle the heavy load. Before starting the construction, engineers follow several important steps to make sure the caisson footing will work well for the project. These steps include checking the ground, installing the caisson, and making sure it’s filled and adjusted correctly.
Site Investigation:
The first step is called site investigation, where engineers study the area to see if caisson footings are needed. They check how strong the soil is, how high the water levels are, and the type of building or structure they plan to build. By analyzing these factors, engineers can decide if the caisson footing is the best option. If the soil is weak and cannot support the building, caisson footing becomes a good choice to make the structure stable and secure.
Caisson Installation:
The next step is caisson installation. Depending on the type of caisson, workers either build it at the construction site or make it ahead of time and move it into place. For example, open caissons are hollow and are sunk into the ground by digging out the soil inside. Builders push the caisson deeper into the earth by removing the dirt, making room for the caisson to reach stronger soil layers. This step is very important to ensure the structure will have a solid foundation.
Excavation and Sinking:
During excavation and sinking, workers dig out soil from inside the caisson as it goes deeper into the ground. This is especially true for open caissons, where workers might enter the caisson to dig by hand or with machines. With pneumatic caissons, workers can safely dig inside because air pressure keeps the water out. The more soil they remove, the deeper the caisson can sink until it reaches the strong layer of soil or rock that can hold up the structure.
Filling the Caisson Footing:
Once the caisson has sunk to the right depth, it is time for filling the caisson. Builders fill the hollow caisson with concrete or another strong material. This filling makes the caisson into a solid, strong base for the structure. The concrete hardens, creating a firm foundation that can handle the weight of the building or bridge. This step is important because it turns the caisson from an empty box into a solid support system.

Final Adjustments:
The last step is final adjustments. After the caisson is filled and in place, engineers check to make sure the structure is level and secure. They check everything carefully to make sure the caisson footing is strong and that the building won’t tilt or shift over time. These small adjustments are very important for keeping the structure safe, stable, and able to last for many years.
When to Use Caisson Footing
Builders mostly use caisson footings when working in water or on very soft ground. In these situations, regular foundations might not be strong enough, so caisson footings provide the needed support. These footings go deep into the ground, reaching stronger layers of soil or rock that can handle the heavy weight of a structure. Now, let’s explore some common cases where caisson footings are the best option.
Bridges:
When building bridges, engineers often use caisson footings to hold up the bridge piers. These piers are the parts of the bridge that stand in water, like rivers or lakes. The soil at the bottom of rivers is usually soft and can’t support the weight of a bridge on its own. By using caissons, builders transfer the weight of the bridge to deeper, stronger ground. This keeps the bridge safe and stops it from sinking or tilting over time.
Marine Structures:
Marine structures, such as piers, docks, and platforms built offshore, also use caisson footings. These structures are often built near water, where the soil is too soft or muddy to hold them up. Caisson footings provide the extra strength needed to keep marine structures steady and safe, even in tough water conditions. Without these footings, piers and docks might move or sink into the soft ground.

High-Rise Buildings:
In cities with loose or soft soil, engineers sometimes use caisson footings to support high-rise buildings. Tall buildings are very heavy, and if the ground below them isn’t strong enough, they can settle or shift, causing damage. Caisson footings solve this problem by transferring the building’s weight deep underground to stronger soil, keeping it straight and secure for a long time.
Dams and Water Retaining Structures:
Dams and other structures that hold back water face huge amounts of pressure. If these structures don’t have a strong foundation, they could crack or even collapse over time. That’s why builders use caisson footings to keep dams stable and secure. The caisson footings transfer the heavy weight and water pressure to deeper, stronger ground, which helps the dam last for a long time without shifting or breaking.
Conclusion
Caisson footings are an essential component of modern construction, particularly for large structures that require deep, stable foundations. From bridges to offshore platforms, these footings ensure that buildings remain secure and supported even in the most challenging conditions. While the process may be complex and costly, the long-term benefits of caisson footing make it a valuable investment for any major construction project.
If you are interested in large construction projects or want to learn about civil engineering, you should understand how caisson footings work.
If you want to know about “The Concrete Friction Coefficient: How It Affects Construction”, Click here
FAQs
A caisson footing is a deep foundation that supports heavy structures. It involves sinking a watertight chamber, or caisson, into the ground to reach strong soil or rock layers for stability.
Builders commonly use caisson footings for structures in water, like bridges and piers, or in places with very soft or unstable soil. They provide extra support to prevent settling or shifting.
The most common types include open caissons, box caissons, pneumatic caissons, and floating caissons. Builders design each type of caisson for specific soil and construction conditions.
In water construction, workers sink caisson footings into the riverbed or seabed until they reach solid ground. They provide a stable base for structures like bridges or marine platforms.
Open caissons are hollow cylinders that are open at the bottom. Box caissons have closed bottoms and are filled with concrete after workers put them in place.
Builders use pneumatic caissons underwater because they have airtight chambers. Where workers can excavate soil safely, with air pressure keeping water out during construction.
Workers usually fill caisson footings with concrete or other strong materials. To create a solid foundation capable of supporting heavy loads.
Workers install caisson footings at different depths, depending on the project. They often sink them deep enough to reach stable soil or bedrock that can hold the structure.
In cities with soft soil, builders use caisson footings to make sure tall buildings have a strong foundation. They prevent the buildings from settling or shifting over time.
Caisson footings provide strong, deep foundations that can support heavy structures. They are ideal for water construction and areas with unstable soil, ensuring long-lasting stability.
